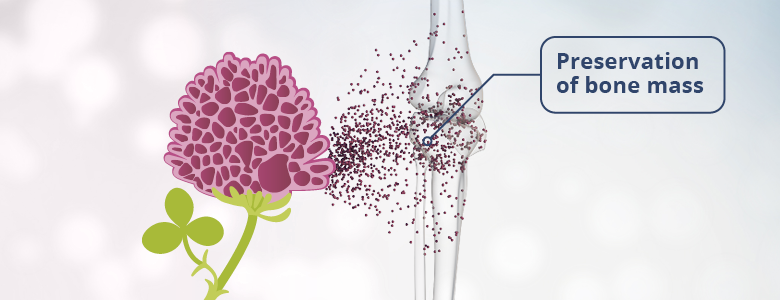
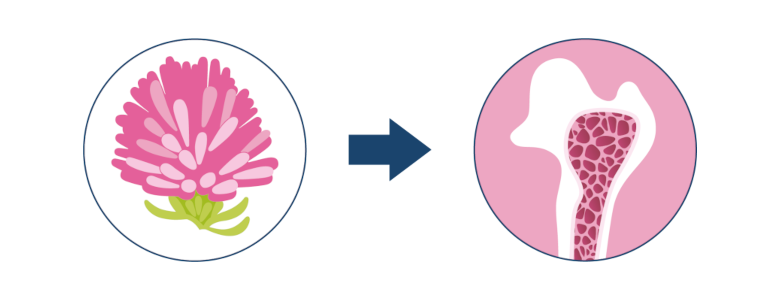
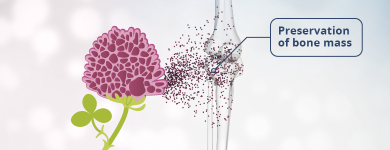
Red clover (Trifolium Pratense) contains isoflavones, which are also known as phytoestrogens. These isoflavones are what make the herb so interesting, as one of the main reasons women are more likely to develop osteopenia than men is that oestrogen production decreases when women reach menopause. Isoflavones from fermented red clover can therefore be used for dietary preservation of bone mass. So, osteopenia is not a disease but a deficiency condition.
The fermentation process
Fermentation is a natural process that has multiple effects.
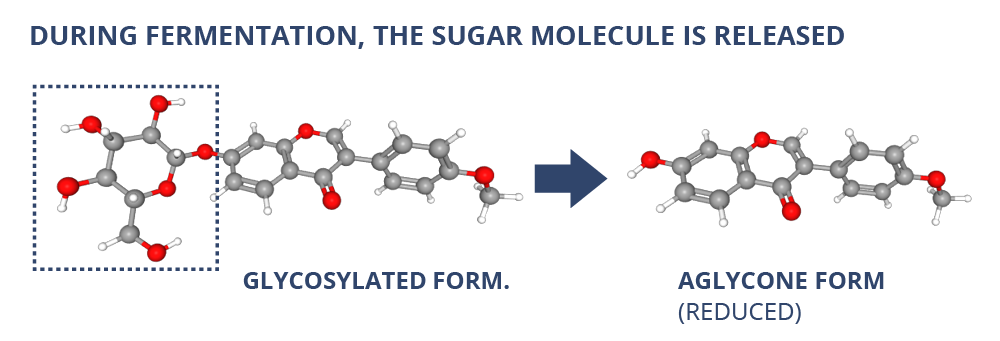
First and foremost, isoflavones are naturally bound to sugar molecules (glucose), also called glycone form. Fermentation results in the release of the sugar molecule, leaving an isoflavone aglycone. This makes it possible for the isoflavones to be absorbed directly into the bloodstream through the intestinal wall. Thus, in the finished fermented extract, more than 90% of the isoflavones are in aglycone form.
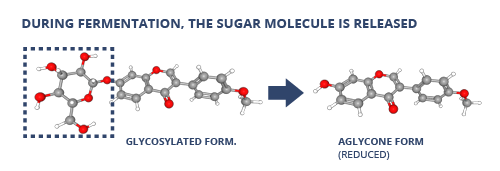
The fermentation then lowers the pH of the extract to around 4, creating an environment where only the lactic acid bacteria that are fermented can survive. The addition of alcohol or other preservatives to the extract is therefore unnecessary.
Last but not least, the extract is not pasteurised, so the live lactic acid bacteria are preserved.
Isoflavones (Phytoestrogens)
Many of the red clover varieties used today have a low isoflavone content. When red clover is to be used for dietary preservation of bone mass, however, it is precisely a high content of isoflavones that we are interested in. At Herrens Mark, we have therefore worked on the sourcing and further development of old red clover varieties for a period.
Effect of isoflavones
Isoflavones belong to the group of substances known as Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERM). This means that the isoflavones prefer to bind to certain types of cells. These are called oestrogen receptors. There are two categories of oestrogen receptors in the body, alpha and beta. The alpha version is mainly found in the breast and uterine tissue. The beta version, on the other hand, is located primarily in the bones, kidneys, lungs and intestines.
Female oestrogen binds primarily to the alpha receptors. Isoflavones, on the other hand, bind 1000 times more strongly to the beta receptors than to the alpha receptors. This means that the isoflavones in red clover prefer to bind to other receptors.
With its active plant substances, isoflavones (Biochanin A and Formononetin), red clover can, in fermented form, be used for dietary preservation of bone mass.